Putting it together: General Linear Models for Decoding#
Show code cell content
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
Show code cell content
import os
from nilearn import datasets
os.environ["NILEARN_SHARED_DATA"] = "~/shared/data/nilearn_data"
datasets.get_data_dirs()
['~/shared/data/nilearn_data', '/Users/emdupre/nilearn_data']
In this final example, we will re-use the code from the previous example to generate statistical maps for each visual category, one per run.
Show code for dataset loading
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_haxby
haxby_dataset = fetch_haxby(subjects=(3,))
# set TR in seconds, following information in the original paper
t_r = 2.5
[fetch_haxby] Dataset found in /Users/emdupre/nilearn_data/haxby2001
Show code for timing information
# Load target information as string
behavior = pd.read_csv(haxby_dataset.session_target[0], sep=" ")
unique_conditions = behavior["labels"].unique()
conditions = behavior["labels"].values
runs = behavior["chunks"].to_numpy()
unique_runs = behavior["chunks"].unique()
# events will take the form of a dictionary of Dataframes, one per run
events = {}
for run in unique_runs:
# get the condition label per run
conditions_run = conditions[runs == run]
# get the number of scans per run, then the corresponding
# vector of frame times
n_scans = len(conditions_run)
frame_times = t_r * np.arange(n_scans)
# each event last the full TR
duration = t_r * np.ones(n_scans)
# Define the events object
events_ = pd.DataFrame(
{
"onset": frame_times,
"trial_type": conditions_run,
"duration": duration,
}
)
# remove the rest condition and insert into the dictionary
# this will be our baseline in the GLM, so we don't want to model it as a condition
events[run] = events_[events_.trial_type != "rest"]
Show code for GLM
from nilearn.image import index_img
from nilearn.glm.first_level import FirstLevelModel
# Instantiate the glm
glm = FirstLevelModel(
t_r=t_r,
mask_img=haxby_dataset.mask,
high_pass=0.008,
smoothing_fwhm=4,
)
z_maps = []
conditions_label = []
run_label = []
for run in unique_runs:
# grab the fmri data for that particular run
fmri_run = index_img(haxby_dataset.func[0], runs == run)
# fit the GLM
glm.fit(fmri_run, events=events[run])
# set up contrasts: one per condition
conditions = events[run].trial_type.unique()
for condition_ in conditions:
z_maps.append(glm.compute_contrast(condition_))
conditions_label.append(condition_)
run_label.append(run)
We now have our statistical maps for each run in the z_maps list.
We also have the visual category type in the conditions_label list,
and the run information in the run_label list.
Using all of these, we can perform a Support Vector Classifier (SVC) analysis using the Decoder object in Nilearn.
from sklearn.model_selection import LeaveOneGroupOut
from nilearn.decoding import Decoder
decoder = Decoder(
estimator="svc",
mask=haxby_dataset.mask,
standardize=False,
screening_percentile=5,
cv=LeaveOneGroupOut(),
)
decoder.fit(z_maps, conditions_label, groups=run_label)
# Return the corresponding mean prediction accuracy compared to chance
# for classifying one-vs-all items.
classification_accuracy = np.mean(list(decoder.cv_scores_.values()))
chance_level = 1.0 / len(np.unique(conditions))
print(
f"Classification accuracy: {classification_accuracy:.4f} / "
f"Chance level: {chance_level}"
)
Classification accuracy: 0.8423 / Chance level: 0.125
decoder.coef_img_
{'bottle': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x140ead940>,
'cat': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x1419150d0>,
'chair': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x141915340>,
'face': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x1419155b0>,
'house': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x141915730>,
'scissors': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x141915790>,
'scrambledpix': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x141915a60>,
'shoe': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image at 0x141915b20>}
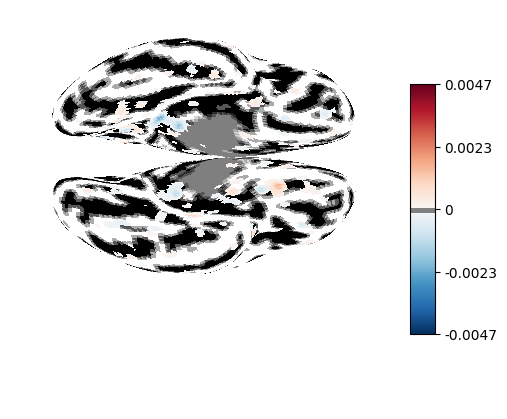
from nilearn.surface import SurfaceImage
from nilearn.plotting import plot_surf_stat_map
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage, load_fsaverage_data
fsaverage_meshes = load_fsaverage()
surface_coef = SurfaceImage.from_volume(
mesh=fsaverage_meshes["pial"],
volume_img=decoder.coef_img_['face'],
)
curv_sign = load_fsaverage_data(data_type="curvature")
for hemi, data in curv_sign.data.parts.items():
curv_sign.data.parts[hemi] = np.sign(data)
plot_surf_stat_map(
surf_mesh=fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
stat_map=surface_coef,
bg_map=curv_sign,
hemi="both",
view="ventral",
threshold=0.0001,
darkness=None,
)

from nilearn.maskers import SurfaceMasker
surf_masker = SurfaceMasker(cmap="viridis").fit(surface_coef)
report = surf_masker.generate_report()
report


